Verified by AI Team
This flow has been practiced in multiple projects, including Apidog integration and OpenAPI spec generation.
API Design Flow
API design follows an API-First approach where the specification precedes implementation, and AI agents generate API specs from high-level requirements combined with design principles.
API-First Principle
API-First Design Flow
Flow Steps
- High-Level Spec - Business requirements and user stories define what the API needs to accomplish
- API Design Principles - Organizational guidelines ensure consistency across APIs
- AI Agent Generation - Agent drafts OpenAPI spec based on inputs
- Human Review - Engineers review for correctness, security, and alignment
- Mock Server - Generate mock server for early consumer validation
- Consumer Validation - Consumers test against mock, provide feedback
- Implementation - Backend implements against approved spec
- Contract Testing - Automated tests verify implementation matches spec
- Documentation - Publish API documentation for consumers
API Specification Platform
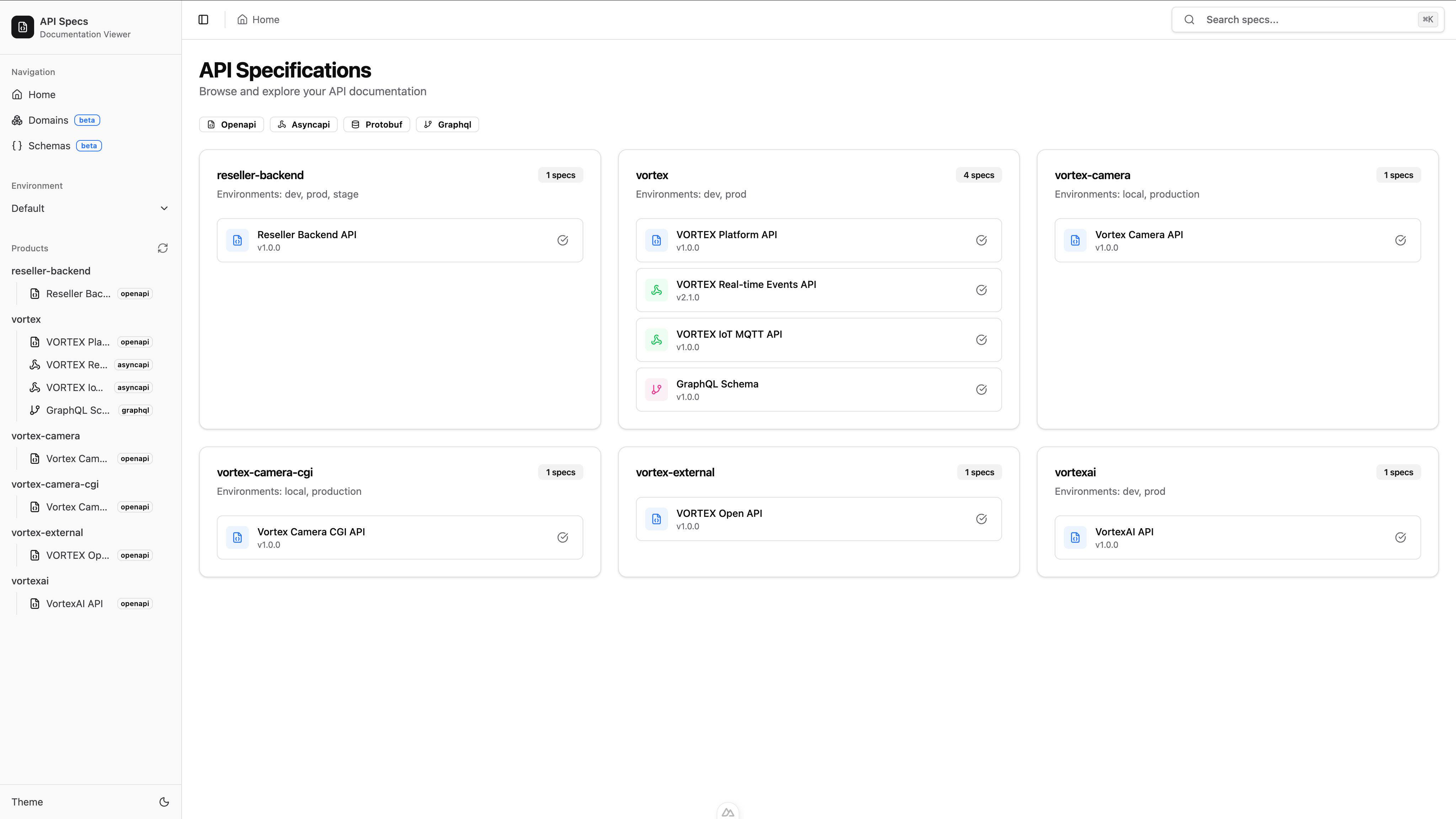
POC Status
This is a proof-of-concept implementation. Additional resources are required for further research and development before production adoption.
Agent Role in API Design
| Phase | Agent Contribution |
|---|---|
| Spec Drafting | Generate OpenAPI from high-level spec + API principles |
| Consistency Check | Validate against organizational API guidelines |
| Mock Generation | Create mock server from OpenAPI spec |
| Test Generation | Generate contract tests from scenarios |
| Integration Analysis | Identify platform constraints from documentation |
| Adapter Generation | Generate adapter interface from integration.md |
API Design Principles (ADP)
Organizations should maintain an API Design Principles (ADP) document that codifies API standards. This document serves as guiding principles for AI agents when reading high-level specs to generate API specifications, preventing context pollution issues such as API spec misalignment.
Reference: An organizational ADP proposal is available at API Design Principle.
ADP Document Structure
# API Design Principles (ADP)
## Naming Conventions
- Resource naming: plural nouns, kebab-case
- Query parameters: camelCase
- Headers: X-Custom-Header format
## Versioning Strategy
- URL path versioning: /api/v1/resources
- Breaking change definition
- Deprecation timeline (minimum 6 months)
## Authentication & Authorization
- Standard auth mechanisms (OAuth 2.0, API keys)
- Token formats and lifetimes
- Scope naming conventions
## Error Response Format
- Standard error schema
- Error code taxonomy
- Localization requirements
## Pagination & Filtering
- Cursor vs offset pagination
- Filter parameter patterns
- Sort parameter format
## Rate Limiting
- Rate limit headers
- Quota policies
- Retry-After behaviorHow AI Agents Use ADP
The ADP document should be:
- Referenced in CLAUDE.md - So AI agents always consider it
- Version controlled - Changes tracked and reviewed
- Enforced via linting - Automated validation against OpenAPI specs
Core Principles
- API-First, always - Spec before implementation; AI generates draft, human approves
- Consumer-driven - Design from consumer perspective, validate with consumers
- Backward compatibility - Breaking changes require deprecation flow
- Consistent conventions - Follow organizational ADP document
- Testable contracts - Every endpoint has contract tests derived from spec
- Platform transparency - Document external platform constraints in integration.md
Anti-patterns
| Anti-pattern | Problem | Correct Approach |
|---|---|---|
| Implementation-first | API design constrained by existing code | Spec defines the contract, implementation follows |
| Undocumented breaking changes | Consumers break silently | Formal deprecation with version migration |
| Inconsistent conventions | Hard to learn, error-prone integration | Follow organizational API style guide |
| Missing error specs | Consumers can't handle failures properly | Define all error responses in spec |
| No consumer validation | API doesn't meet actual needs | Test with mock server before implementation |
Related: Workflow Framework Overview